Oyster Reef Program Regenerates New Life In Bay
News Staff • March 24, 2025
Scientists and volunteers unite to restore oyster reefs
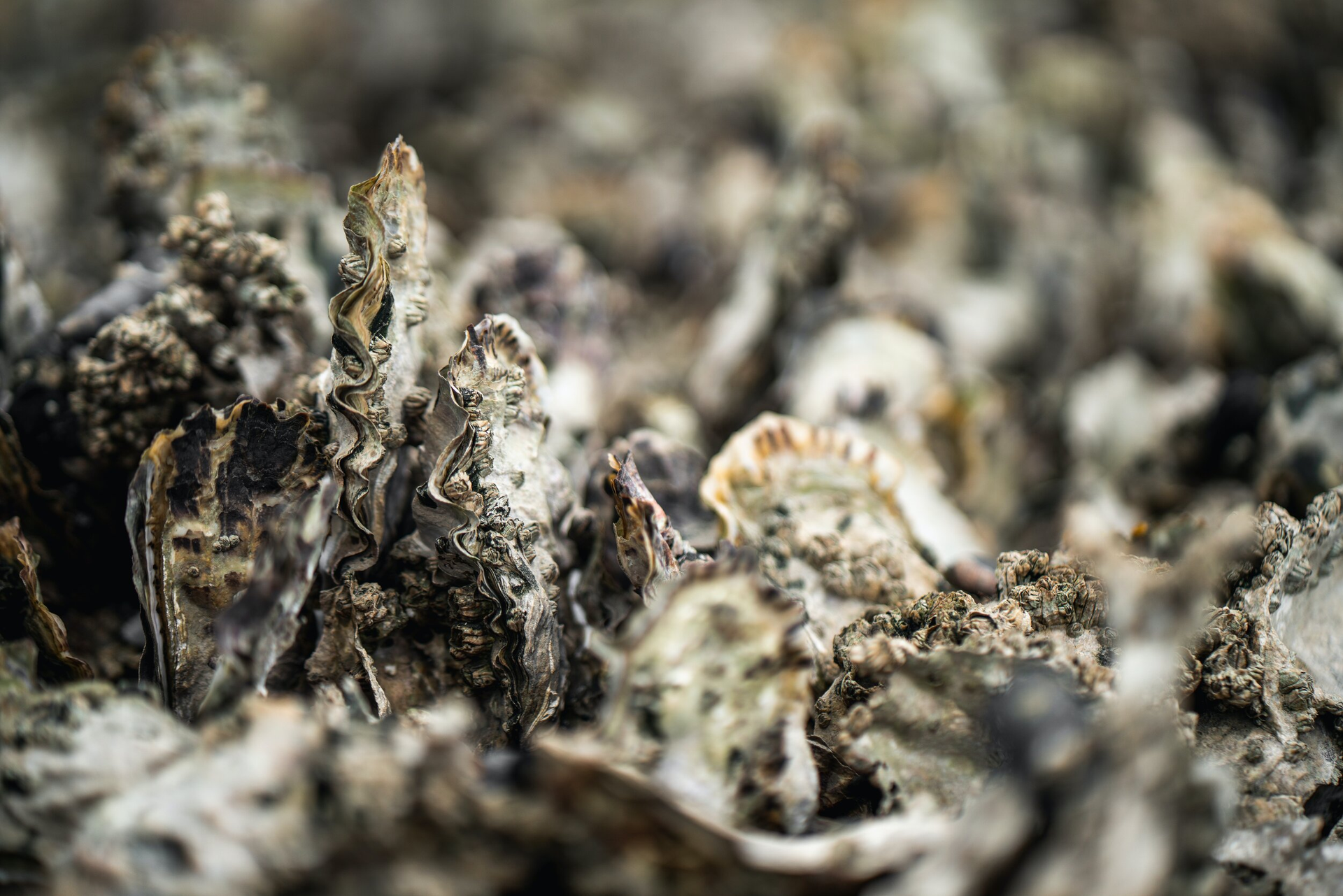

Mobile Bay’s oyster population is getting a much-needed boost, thanks to the efforts of the Oyster Keepers program. This year alone, the program has successfully introduced 61,000 oysters back into the bay, contributing to the restoration of vital oyster reefs that serve as the backbone of the local marine ecosystem.
The Importance of Oysters in Mobile Bay
Oysters play a critical role in estuary health, acting as natural water filters and providing habitat for various marine species. Their presence strengthens the local ecosystem while also supporting Alabama’s coastal traditions.
“Oysters are a vital keystone species in estuaries and are a cultural touchstone for coastal Alabamians,” said Dr. Kayla Boyd, Oyster Project Manager. “By collaborating with volunteer piers and the Auburn University Marine Extension and Research Center, Oyster Gardening is increasing the number of live oysters being returned to the bay each year. I'm looking forward to seeing the reefs continue to grow.”
A Community Effort for Restoration
The success of the Oyster Keepers program highlights the power of community collaboration. Volunteers, researchers, and conservation groups have worked together to restore these reefs, ensuring they remain a thriving part of the bay’s ecosystem for generations to come.
"Restoring our oyster reefs takes a community effort, and we are committed to working with our partners across Mobile Bay to ensure that our reefs survive and thrive," Dr. Boyd emphasized.
A special thank-you goes out to Impact 100 Baldwin County, whose funding has made this year’s success possible. Their support ensures that oyster restoration continues to be a priority in Mobile Bay.
Ancient Oyster Consumption and the Legacy of Shellbanks
Humans have been eating oysters for at least 164,000 years! Archaeological evidence from coastal caves in South Africa shows that early humans were harvesting and consuming oysters and other shellfish as far back as the Middle Stone Age.
Oysters have been an essential food source across many ancient civilizations, including the Romans, Greeks, Chinese, and Indigenous peoples worldwide. The Romans, for instance, were so fond of oysters that they developed early aquaculture techniques to farm them. Similarly, Indigenous tribes along North America's coasts sustainably harvested oysters for thousands of years, leaving behind shell mounds known as middens, which provide insights into ancient diets and environmental changes.
Along the Alabama Gulf Coast, Native American tribes, including the Mississippian and Creek peoples, gathered oysters as a major part of their diet. Over time, they created massive shell mounds, known as Shellbanks, in areas like the ones in Gulf Shores. These ancient structures, made up of discarded oyster shells and other remnants of daily life, serve as historical markers of the region's rich Indigenous heritage and their deep connection to the coastal environment.
So, oysters have been a staple food, cultural symbol, and even a luxury delicacy for tens of thousands of years!
Learn More and Get Involved
To learn more about Mobile Bay’s native oysters and the Baykeeper’s Oyster Keepers Program, visit: Oysters of Mobile Bay